Real-time incremental explanations for object detectors Under Review
Abstract
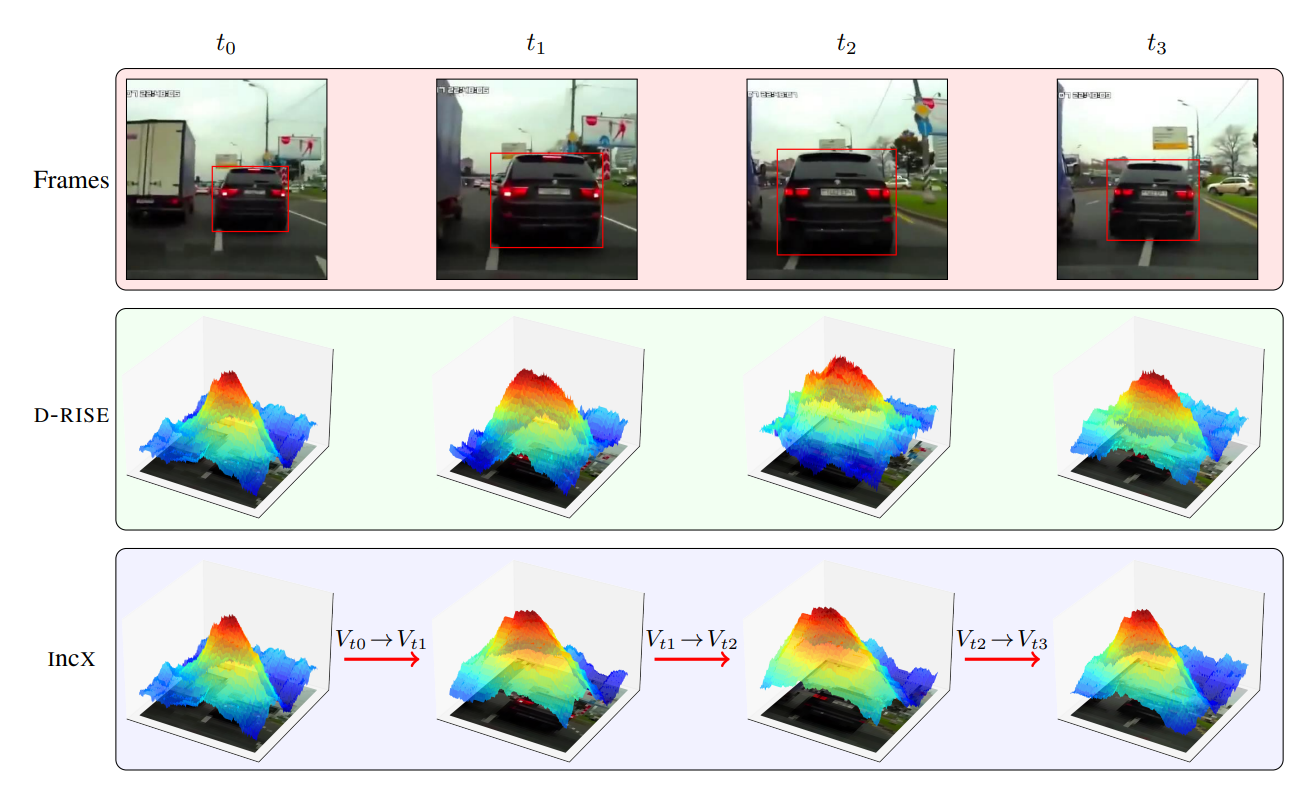
Existing black-box explainability tools for object detectors rely on multiple calls to the model, which prevents them from computing explanations in real time. In this paper, we introduce IncX, an algorithm for real-time incremental approximations of explanations, based on linear transformations of saliency maps. We implement IncX on top of D-RISE, a state-of-the-art black-box explainability tool for object detectors. We show that IncX’s explanations are comparable in quality to those of D-RISE, with insertion curves being within 8%, and are computed two orders of magnitude faster than D-RISE’s explanations.
Methods
We leveraged computer vision definitions to mathematically prove that the proposed linear transformation of the saliency map can be represented by rigid transformations of the 3D object. In addition to that, we performed our experiments on a subset of LaSOT dataset for three models, being YOLOv10, Faster-RCNN, and RT-DETR. We compute classic metrics for explainable AI algorithms, such as insertion and deletion to measure the performance of our algorithm.
Results
The insertion values for IncX are consistently within 8% of those observed for D-RISE, with all other metrics displaying similar trends. Moreover, the computation time for IncX is two orders of magnitude lower than that of D-RISE (111 times faster for Faster R-CNN), highlighting the suitability of IncX for real-time scenarios. In addition, when measuring the similarity between the original explanations produced by D-RISE and the ones produced by IncX, we can see that the results show a clear similarity between the approximations implemented by IncX and the original saliency maps created by D-RISE.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that IncX operates in real time, with negligible overhead over the object detector and is two orders of magnitude faster than generating a new saliency map. Moreover, IncX produces saliency maps closely aligned with freshly computed maps, achieving an average correlation coefficient of approximately 0.8 across all models used, with minimal computational overhead. The quality metrics for assessing explainable AI algorithms show that IncX is comparable to D-RISE, with the insertion score within 8% of D-RISE’s ones.
IncX handles linear transformations of objects; future work will address the current limitations related to rotation and object deformation. We anticipate future applications of this algorithm in various industries, particularly in self-driving cars.
How to cite this work:
@misc{calderónpeña2024realtimeincrementalexplanationsobject, title={Real-Time Incremental Explanations for Object Detectors}, author={Santiago Calderón-Peña and Hana Chockler and David A. Kelly}, year={2024}, eprint={2408.11963}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.CV}, url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.11963}, }